PyX — Example: drawing2/smoothed.py
Smoothing paths
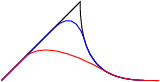
from pyx import * c = canvas.canvas() p = path.line(0, 0, 2, 2) p.append(path.curveto(2, 0, 3, 0, 4, 0)) c.stroke(p) c.stroke(p, [deformer.smoothed(1.0), color.rgb.blue]) c.stroke(p, [deformer.smoothed(2.0), color.rgb.red]) c.writeEPSfile("smoothed") c.writePDFfile("smoothed") c.writeSVGfile("smoothed")
Description
This example shows how to use the deformer class. A deformer takes an original path and return a modified one, which is here a smoothed variant. The deformer can be used like any other attribute when stroking or filling a path.
Here, we show the use of deformer.smoothed, which smoothes away corners in the original path. It operates on the pathitems of the original path and cuts out pieces of a given length (1.0 in the example) surrounding a corner and replaces them by a smooth curve. This new curve is determined to be geometrically smooth, exhibiting the same tangents and curvatures as the original path at the connection points. Alltogether, the smoothing is performed not in a strictly geometrical sense but also depends on the parameterization of the path. If you try to smooth a path consisting of many short path elements, nothing will really change.
In all deformers, the deformed path can be accessed directly by
ps = deformer.smoothed(1.0).deform(p)